Psoriasis or psoriasis is a chronic disease that affects the skin and its appendages: the hair and nails. Characterized by periods of worsening condition (relapses) and temporal well-being when symptoms of disease become less. This disease is not infectious and the patient is not dangerous to others. Because the appearance of psoriasis is not associated with the microorganisms.
Psoriasis often occurs between the ages of 15-45 years. It more affects people with fair skin. In developed countries, the number of patients with psoriasis reaches 2-4% of the population. It suffers from every 25th inhabitant of the earth on all continents.
This issue deals with a huge number of medical institutions. Therefore psoriasis has become the most studied disease. But still this disease is not fully understood. Officially, it is considered incurable and raises many questions.
Psoriasis is called by its own immune cells of the body. They rise from the lower layers of the skin at the top, causing inflammation, proliferation of epidermal cells and the formation of small capillaries.
Symptoms of psoriasis on the skin are quite diverse. Most often disease causes of red spots of psoriatic plaques. They are dry to the touch, rise above the skin surface and covered with white bloom.
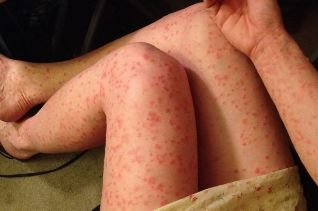
Types of psoriasis
The disease is divided into two large groups: pustular and non-pustulous psoriasis.
Non-pustulous psoriasis
- ordinary (vulgar) or simple psoriasis (plaque-like psoriasis, chronic stable psoriasis)
- psoriatic erythroderma psoriasis or erythrodermal
Pustular psoriasis
- pustular psoriasis von Tsumbush or generalized pustular psoriasis
- palmoplantary psoriasis (pustular psoriasis of the extremities, chronic persistent palmoplantary pustules)
- annulary pustular psoriasis
- Palmar-plantar psoriasis
- herpetiform psoriatic impetigo
Additionally there are the following types of psoriasis
- seborrheic psoriasis
- psoriasis flexor surfaces and skin creases
- psoriasis Napkin
- psoriasis caused by medications
By severity distinguish such forms of psoriasis
- Light – struck less than 3% of the skin.
- Moderate 3-10% of the skin covered with plaques.
- Heavy – there is joint damage, or involved more than 10% of the skin.
Causes of psoriasis
To date there is no unequivocal answer to the question: "why do I get psoriasis?". Scientists put forward several theories.
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease. It is based on the failure of the immune system. Immune cells T-killers and T-helpers, the function of which is to protect the body from viruses, bacteria and tumor cells, for some reason, penetrate into the upper layers of the skin. Here they produce inflammatory mediators – substances that trigger the inflammatory response. The outcome is enhanced skin cell division and multiplication (proliferation).
Psoriasis is a disease which is caused by the impaired growth, division and maturation of epithelial cells - keratinocytes. The result of these changes in the skin becomes attack immune cells, T-lymphocytes and macrophages in the diseased cells of the skin.
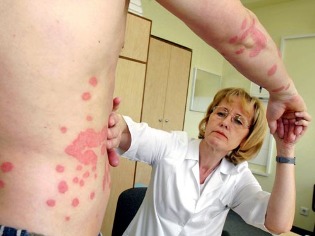
Factors that contribute to the development of psoriasis
The doctors noted a number of factors that can cause disease. Of course, most often the psoriasis occurs when the body acts on several such conditions.
- Genetic predisposition. There is a theory that genes responsible for the immune system and the function of T-lymphocytes are the carriers of the disease. Therefore, parents who suffer from psoriasis, the probability to give birth to children who will develop the same symptoms.
- Thin dry skin. It was noted that people with these characteristics of the skin suffer more often than those with oily skin and well hydrated. This is probably due to the protective function of sebum and characteristics of the structure of the skin.
- External irritants. A high percentage of patients among those people who are constantly in contact with alcohol solutions, solvents, household chemicals, cosmetics (lotions, cream for the hands).
- Excessive hygiene – excessive love to cleanliness also undermines protective properties of the skin. Soap, shower gels and washcloths wash away natural protective barrier and leave behind a microscopic injury.
- Bad habits – alcohol, Smoking and drugs is bad for the skin. It worsens blood circulation and nutrition.
- HIV – AIDS patients are more prone to the occurrence of psoriasis. Scientists can not explain this phenomenon. The fact that psoriasis is caused by increased activity of lymphocytes and AIDS, their number decreases.
- Medications – some medications can trigger the disease. Among them are: beta-blockers, antidepressants, anticonvulsants and antimalarial medications, lithium carbonate.
- Infection (fungi and Staphylococcus aureus). Quite often there have been cases when the psoriasis appeared immediately after fungal infections or diseases caused by Streptococcus.
- Moving – change of climate or even the time of year, the deterioration of the environment can be a trigger for this disease.
- Stress is a strong emotional shock or physical stress (prolonged periods of hypothermia, overheating, accidents) precede the appearance of the first symptoms of psoriasis.
- Injury permanent effects on the skin: pressure, friction, scratching. This regular injury can cause at this place for the first psoriatic plaques.
- Allergic conditions – allergic skin rash and processes that occur at the same time, in all layers of the skin, also increase the risk of disease.
What are the symptoms and signs of psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a systemic disease that affects not only the skin and nails. It affects the joints, tendons, and spine, immune, nervous and endocrine systems. Often affects the kidneys, liver, thyroid. The patient feels fatigued, suffers from chronic fatigue and depression. Such a complex effect on the body, the disease in recent years is called psoriatic disease.
But still the main manifestations of the disease occur on the skin. The name "psoriasis" is quite accurately conveys the symptoms of psoriasis. The first manifestations often become papules are pink or bright red color, rounded shape, covered with scales – psoriatic plaques. They are located symmetrically, mostly on the extensor surfaces, lower back and scalp. But can affect any areas of the skin and genital mucosa. Their size from a few millimeters, in the initial stages, up to ten centimeters or more.
Depending on the characteristics of the rash, share this form of psoriasis:
- Point psoriasis is the size of the elements smaller than a pinhead.
- Guttate psoriasis papules are shaped like tears and reach the size of a grain.
- Nummular psoriasis is plaques grow to 3-5 mm and have rounded edges.
Also there are forms of the rash when its elements have the form of rings, arcs, and garlands, maps with jagged edges.
Papules covered with a coating that is easily removed. It consists of keratinized epidermal cells. Psoriatic plaques begin to be covered with scales from the center, then RAID is spread to the edges. It is loose and light appearance due to the fact that keratinized cells are permeated by spaces filled with air. Around elements can be formed a pink ring is the site of inflammation, the growth of plaque. The skin around the lesions is not changed.
Under the touch detected by the shiny smooth bright red surface. This blood capillaries with thin walls, covered with a thin film. They become visible due to thinning of the upper layers of the skin. The normal structure of the skin is broken due to the fact that the cells of the keratinocytes Mature and normally do not have time to differentiate.
Psoriasis scalp is a psoriatic plaques that significantly rise above the surrounding skin. They are densely covered with scales, resembling dandruff. While the hair is still not impressed. The rash can be not only for hair, but smooth skin on the neck and behind the ears. These changes are explained by the active division of the keratinocytes in the affected areas
Psoriasis feet and palms causes severe thickening of the Horny layer of the skin in these areas of the body. The skin becomes thick, rough. Often permeate the cracks. It's caused by intensive cell division, which multiply up to 8 times faster than normal, but not removed in time from the surface of the skin.
Nail psoriasis is characterized by a variety of symptoms. But the most important are two main types of lesions of the nail plate:
- The type of "thimble". On the nail plate are formed small holes, like needle marks needle.
- The type of onychomycosis. Lesions resemble the fungus on the nails. The nails thicken, discolor, peel. Through the nail plate is visible psoriatic papule surrounded by a red rim. She has the appearance of oil spots seen through the nail.
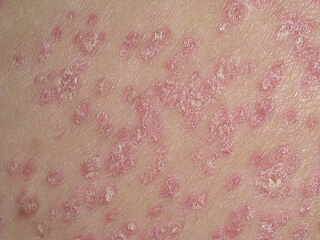
Symptoms and signs of psoriasis depend on the stage of the disease, which alternate cyclically throughout the year. Since the majority of patients have a "winter" type of the disease, when exacerbation is necessary for autumn and winter. Improvement in summer is due to the fact that ultraviolet light in sunlight has a therapeutic effect. But some patients suffer "summer" type.
There are such stages of psoriasis:
- progressive – the emergence of new elements, the active growth of existing plaques, pink growth zone around them, intense flaking and itching.
- stationary – stop growth of the papules, the absence of new lesions, small folding the top layer of skin around the psoriatic plaques.
- regressing– no peeling, the disappearance of the plaques and the appearance in their place, areas of pigmentation, evidence of the attenuation process.
How to look skin rashes psoriasis?
Every body is different and reacts differently to the disease. Therefore, the nature of lesions can be very diverse. This explains the diversity of forms and types of psoriasis.
However, most people symptoms of psoriasis are similar. It stains red psoriatic plaques, rising by 1-3 mm above the level of healthy skin. Their appearance is caused by the fact that the cells of the superficial layer of the skin – keratinocytes, divide very actively, not having time to Mature and become a full-fledged skin cells. As a result of this enhanced pathological growth of individual areas of the skin thicken. This occurs under the influence that immune cells secrete chemicals that cause inflammation in the skin.
The spots are red in color. And if you remove the top scales psoriasis patches, its surface begins to be covered in blood dew. This is due to the fact that under the influence of T lymphocytes and immune dendritic cells is increased formation of new blood vessels under the plaque. They have a fairly thin wall. This causes bleeding of psoriatic plaques at the slightest damage.
Sometimes through the walls of the vessels is leaking lymph and inflammatory exudate. The crust is on the plaque becomes thick, yellowish. The surface on touch moist.
On top of the plaques can be covered with a gray, silver or yellowish coating that has the appearance of wax. Therefore, they are called "paraffin lakes". It's dead skin cells, the rejection of which is broken, and they accumulate on the surface of the affected area of the skin.
Spot peel, hotter to the touch than the rest of the skin, can reach large sizes. Often the patient experiences severe itching in this place. This is due to the fact that on the background of inflammatory process there is a cascade of neuro-reflex reactions and allergic reaction.
Another type is the papules. This small lesions resembling tubercles. The size is about 1 mm. In the middle there is a cavity filled with content. Often they are located in the knee and elbow joints. They remain even during periods when the disease is retreating.
The first plaques occur in areas where the skin is drier and contact with household chemicals and detergents – in the open areas of arms, neck. They can be on any part of the body: scalp, face, trunk, genitals, buttocks, legs. Unlike fungal diseases, psoriasis rashes do not occur in the armpits and the natural folds where the skin is more moist and fatty. In some forms of the disease appears only a few plaques that do not increase in size. When hand-foot shaped lesions are only on these sites.
During exacerbations the lesions gradually grow in width and merge with the neighboring plaques. During periods of improvement (remission) spots begin to lighten from the middle. They gradually acquire the form of a ring and can completely dissolve. After the plaques on the body leaves marks – pigmentation. It can be significantly lighter or darker than the surrounding skin. Once people get a tan, skin color is usually aligned.























