Psoriasis is a disease due to which the skin appears red, peeling and a Horny rash covered with silvery-white scales.
Usually these rashes appear on the elbows, knees, the skin hair of the head and on the lower part of the back, but can be observed in other places. For most people, the small rashes. In some cases they can itch or hurt.
In Russia with psoriasis get sick about 1% of the population, often psoriasis occurs among the indigenous population of the north. Men and women suffer equally often. First symptoms of psoriasis occur more often under the age of 30 years, but later the beginning of psoriasis is not uncommon. The severity of psoriasis for each person is different. Someone psoriasis just a little bit uncomfortable, while other people psoriasis prevents lead a normal life.
Psoriasis — is a chronic disease in which there is usually a period of remission — asymptomatic or with a few prominent symptoms, after which come the period of exacerbation, when symptoms become more pronounced.
Psoriasis occurs when the acceleration of the process of reproduction in human body skin cells. Skin cells are normally produced changes every 3-4 months, but with psoriasis this process is shortened to 3-7 days. As a result — creates a buildup of skin cells, which leads to the formation of the characteristic changes on the body.
Causes of psoriasis to the end is not clear, it is believed that the increased reproduction of skin cells is caused by a disorder of the immune system. Immune system — natural protection of the organism against infection and disease, but in people with psoriasis, it mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells.
Scabies can be transmitted by inheritance, and therefore believed that in this disorder there is a genetic factor. So far, however, it is not clear exactly what role is played by genetics in the emergence of psoriasis.
In many people the symptoms of psoriasis or appear another after a certain event, which is called the trigger. Possible triggers of psoriasis include damage to the skin, infectious diseases of the throat and intake of certain medications. This disease is not contagious and cannot be passed from one person to another.
When a suspected psoriasis you should seek medical help. Often the doctor can make a diagnosis judging from the appearance of your skin. Usually for the diagnosis and treatment of psoriasis of the patient to refer to a dermatologist — specialist in skin disease.
Even when you treat the psoriasis is not possible, there are a number of treatments that can relieve its symptoms and improve the overall appearance of the skin. In most cases, in the first place is intended for local treatment, for example, analogues of vitamin D or corticosteroids local action. In the most severe cases, when not helping other treatment methods, can exercise systemic treatment. Systemic treatment — that is the reception inside or in the form of injected drugs that have a therapeutic effect on the whole organism.
For some people psoriasis — just a small problem, but sometimes it can greatly affect your life. For example, some patients with psoriasis have low self-esteem because of how the disease affects their appearance. Often also with psoriasis appear painful sensitivity, pain and swelling of the joints and connective tissue. This is called psoriatic arthritis.
The symptoms of psoriasis
In most cases, psoriasis runs through the bike: every couple of weeks or months, the disease continues to deteriorate, and then, the symptoms are less visible or disappear, and there comes a remission.
There are several different types of psoriasis. Many sufferers are only form of psoriasis, although it is possible the disease two different types at the same time. One type may develop into another species, or worsen. When a suspected psoriasis you should seek medical help.
The most common types of psoriasis
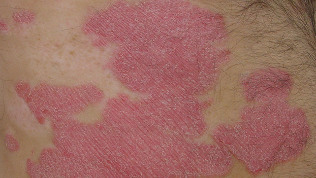
Common psoriasis. It is the most common form of psoriasis, accounting for about 90% of all cases. Symptoms — dry red skin growths called plaques covered with silvery-white scales. They usually appear on the elbows, knees, the skin hair of the head and on the lower part of the back, but can also occur in other places. Food stamps may itch or hurt. In severe cases, the skin at the joints may crack and bleed.
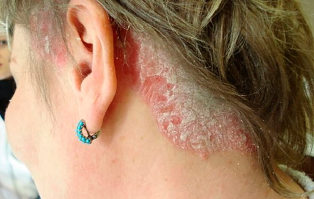
Psoriasis of scalp (seborrheic psoriasis) can occur on the scalp or on adjacent areas of the skin, as well as on the back and chest. Causes reddish rashes, covered by dense silvery-white scales. For some people, this type of psoriasis causes severe itching, while others it does not cause any difficulties. In the most severe cases can lead to hair loss, most often temporary.
Psoriasis of the nails. Approximately half of the patients with psoriasis, the disease spreads to the nails. With psoriasis in your nails may appear small fossa or deepening, may lose color and shape. Often nails can be released and depart from the nail bed, in which they are located. In severe cases, nails may crumble.
With psoriasis in the form of drops appear small (less than 1 cm) plaque in the shape of drops on the chest, hands, feet and under the hair on his head. There is a high probability that the teardrop psoriasis fully will be held in a few weeks, but in some people it turns into an ordinary psoriasis. This type of psoriasis sometimes occurs after strep infection in the throat, and they are more likely to fall ill children and youth.
Psoriasis folds - affects skin folds, for example, under the arms, in the groin, between the buttocks or under the milk glands. They may appear large smooth rashes in some or in all of these areas. Symptoms have sharpened in friction and sweating, so it can deliver a certain discomfort in hot weather.
Pustular psoriasis
More about a rare type of psoriasis in which the skin appear blisters (bubbles with purulent content). Different types of pustular psoriasis affect different parts of the body.
Generalized pulstole psoriasis (psoriasis von Tsumbush). Pustules occur on large areas of skin and evolve very quickly. The pus consists of white blood cells and its appearance is not always directly associated with the infection. Pustules may be cyclic appear repeatedly every few days or weeks. At the beginning of these cycles psoriasis background Tsumbush can cause fever, chills, weight loss and chronic fatigue.
Palmar-plantar psoriasis. Pustules appear on the palms and soles of the feet. Gradually turning into pustules rounded brown plaques with scales, which are then separated from the skin. Pustules may appear repeatedly every few days or weeks.
Pustular acrodermatitis (acrobustulosis). Pustules appear on the fingers hands and feet. Then the blisters burst, they remain bright red areas that may secrete fluid, or covered by scales. Can lead to a painful deformation of the nails.
Erythrodermic psoriasis (psoriatic erythroderma)
Erythrodermic psoriasis is a rare form of psoriasis, which affects practically the whole of the surface of the skin. It causes severe itching or burning. Because of erythrodermic psoriasis your body can lose proteins and fluid. This can lead to the emergence of other complications, such as infection, dehydration, heart failure, hypothermia and exhaustion.
Causes of psoriasis
Psoriasis occurs when skin cells divide and are updated faster than usual. Causes of psoriasis to the end is not clear. The body produces new cells in the deepest layer of the skin. These cells gradually move upwards. Coming to the surface, they die. This process is in the standard takes place gradually and unnoticeably for us. The skin cells are updated once every 3-4 weeks.
In people with psoriasis this process takes only 3-7 days. Consequently, it is not yet fully these body parts cells rapidly accumulate on the surface of the skin, which causes the formation of red, peeling and stratum of the rash covered with silvery-white scales. It is believed that in patients with psoriasis the skin cells are changing faster due to a malfunction of the immune system.
The immune system is the defense of the body, which helps him fight infections. One of the basic types of cells, which uses the immune system, called T-lymphocytes.
T-lymphocytes are usually moving in the body detects the infection and fight with them. In people with psoriasis mistakenly attack the healthy skin cells. This forces the immune system to produce more T-lymphocytes as well as play new skin cells faster than usual.
Up to the end is not clear what exactly causes the disorder of the immune system, although it may be that the role in that play some of the genes and environmental factors.
Psoriasis is hereditary. One out of three patients with psoriasis has a close relative with the disease. So far, however, it is not clear exactly what role is played by genetics in the emergence of psoriasis. The results of the study indicate that, for the development of psoriasis may meet in many genes. Most likely, make a person more susceptible to this disease can their different combinations. However, it is hereditary it is not alone psoriasis, but only the predisposition to it, this means that the presence of these genes does not mean that you necessarily will develop the disease.
Triggers of psoriasis
In many people the symptoms of psoriasis or appear another after a certain event, which is called the trigger. If you know your triggers, and it can help avoid worsening of symptoms. Examples of the most common triggers:
- damage to the skin, for example, cut, scratch, insect bites or sunburn (the so-called phenomenon of Kebner);
- the abuse of alcohol;
- smoking;
- stress;
- hormonal changes, especially in women (e.g. at the time of the pubertal period and at the menopause);
- some drugs, for example, lithium, some anti-malaria drugs, anti-inflammatories, including ibuprofen, ACE inhibitors (to treat ), and beta-blockers (to treat heart failure);
- infection in the throat — for some people, especially in children and young people, after a strep infection in the throat develops a form of psoriasis, which is called the teardrop psoriasis, although in most cases after a strep infection in the throat psoriasis arises;
- other immune system disorders, such as HIV, causing the emergence or worsening of psoriasis.
Psoriasis is not contagious and therefore cannot be passed from one person to another.
Diagnosis of psoriasis
As usual for a diagnosis of psoriasis enough external inspection of the skin.
In more rare cases it is necessary to taking a biopsy (small sample of skin), which then dispatched to the laboratory for study under a microscope. This will allow to identify the specific type of psoriasis and rule out other skin diseases, like seborrheic dermatitis, lichen red haze, a simple chronic disease, and a pink haze.
Usually, the diagnosis and treatment of psoriasis is carried out under the supervision of a physician-dermatologist — specialist in skin disease. If the doctor suspects you have psoriatic arthritis, which sometimes arises as a complication of psoriasis, you can send it to a rheumatologist. Rheumatologist — a physician who specializes in arthritis.
You can take blood tests to rule out other diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, but also to take x-rays of the joints affected by the disease.
Treatment of psoriasis
Completely cure psoriasis is not possible, however, with the help of treatment can reduce the severity and frequency of exacerbations. Usually the treatment of psoriasis takes place under the supervision of a dermatologist, in case of involvement in the process of the joints named the consulting rheumatologist. If the symptoms of psoriasis significantly expressed and poorly respond to treatment, your doctor may refer you for hospitalization in the hospital, in the department of dermatology.
One or another method of treatment is used depending on the type and severity of the psoriasis and area of skin covered by the disease. If the symptoms of psoriasis are expressed slightly and is not increasing, the physician, perhaps, is the limited indication of the external resources, for example, in the form of a cream. At the stage of exacerbation usually associated with more serious treatment with drugs, was taken in the inside.
There is a wide range of resources for the treatment of psoriasis, but it can be difficult to determine exactly what drug the most effective. Talk to your doctor, if you feel that the treatment isn't working or you have side effects that cause annoyance.
Methods of treatment are divided into 3 categories:
- topical treatment on the skin applied creams and ointments;
- phototherapy — your skin is irradiated with a certain type of uv radiation;
- system — reception inside, or in the form of injected drugs that have a therapeutic effect on the whole organism.
Often different methods of treatment in combination. So as sick with psoriasis requires longer treatment, it makes sense to assemble a work plan of medicinal manipulation, which should be a day to do. The doctor should regularly check your health status, and, if necessary, adjust the treatment plan.























